what is behavioral targeting: A quick guide to targeted ads
Think of it like a great shop assistant who remembers what you like. The one who doesn't show you sweaters when you're clearly looking for running shoes. That's what behavioral targeting does online. It's a strategy that looks at your digital footprint—the articles you read, the products you click on, the videos you watch—to show you ads that actually make sense for you.
Unpacking Behavioral Targeting
At its heart, behavioral targeting is about moving away from the old "spray and pray" method of advertising. Instead of blasting a single generic message to millions, it’s about listening to what people's actions are telling you and tailoring the experience accordingly. The whole idea is built on a simple truth: what you've done in the past is the best clue to what you'll do next.
This marketing strategy analyzes how users behave online—their search queries, the content they consume, their purchase history—to deliver personalized ads. It works by collecting data from websites and apps to group audiences based on things like buying intent and browsing habits. And it works. This kind of targeted advertising pulls in, on average, 2.7 times more revenue per ad compared to ads that aren't targeted. You can dig into more data on behavioral advertising results on Jake Jorgovan's blog.
Behavioral Targeting Compared to Other Methods
To really get what makes behavioral targeting unique, it helps to see it side-by-side with other common ad strategies. Each one uses different data to find an audience, but their aim and accuracy are worlds apart.
| Targeting Method | What It Tracks | Primary Goal | Actionable Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Behavioral | Individual user actions (clicks, views, purchases) | Personalize ads based on proven interests and intent. | Showing ads for running shoes to a user who recently read articles about marathon training. |
| Contextual | Website or page content (keywords, topics) | Place ads alongside relevant content, regardless of the user. | Displaying an ad for a new video game on a game review blog. |
| Demographic | User attributes (age, gender, location, income) | Reach broad audience segments based on static characteristics. | Advertising luxury cars to individuals in high-income postal codes. |
As you can see, each method has its place, but they operate on fundamentally different assumptions about the user.
The Actionable Difference: From Guessing to Knowing
The real takeaway here is the level of personalization. Demographic targeting is basically an educated guess (“people in this age group probably like this”). Contextual targeting aligns with a topic (“someone reading about cooking might need new pans”). But behavioral targeting acts on proven interest.
Behavioral targeting doesn't just guess what you might like; it responds to what your actions have already told it you're looking for. This makes the ads you see less of an interruption and more of a helpful suggestion.
This direct line to user behavior is what makes the strategy so powerful. It lets brands connect with potential customers at the precise moment their interest peaks, turning a passive browse into a real chance to engage.
How Behavioral Targeting Technology Works
To really get what behavioral targeting is, you have to peek behind the curtain at the tech making it all happen. Think of it as a digital detective story. It follows clues—your clicks, your views, your time spent on a page—to solve the mystery of what you actually want. The whole thing is a slick cycle of data collection, analysis, and action that unfolds in milliseconds.
It all starts with data collection. When you land on a website, tiny text files called cookies get stored in your browser. These cookies are like digital breadcrumbs, remembering where you've been, what you looked at, and what you tossed in your shopping cart. Marketers also use pixels—basically invisible, single-pixel images embedded in web pages or emails—to track specific actions, like opening a message or finishing a purchase.
From Raw Data to Audience Segments
All this raw behavioral data is interesting, but its real magic is unlocked through organization. The next step is audience segmentation, where the system groups users with similar patterns into distinct buckets. At its core, behavioral targeting tech is all about analyzing and categorizing user actions, which requires a deep understanding of user segments and events.
For example, someone who’s constantly reading articles about marathon training and buying athletic gear might land in an "Active Runner" segment. Another person browsing mortgage calculators and local real estate listings? They could be flagged as a "Potential Home Buyer." This lets marketers ditch generic assumptions and instead target groups based on what they've proven they're interested in. It’s the engine that powers real personalization, something we dig into deeper in our guide to marketing personalization strategies.
This flow chart gives you a bird's-eye view of how user data is collected, segmented, and ultimately used to show you ads that feel relevant.
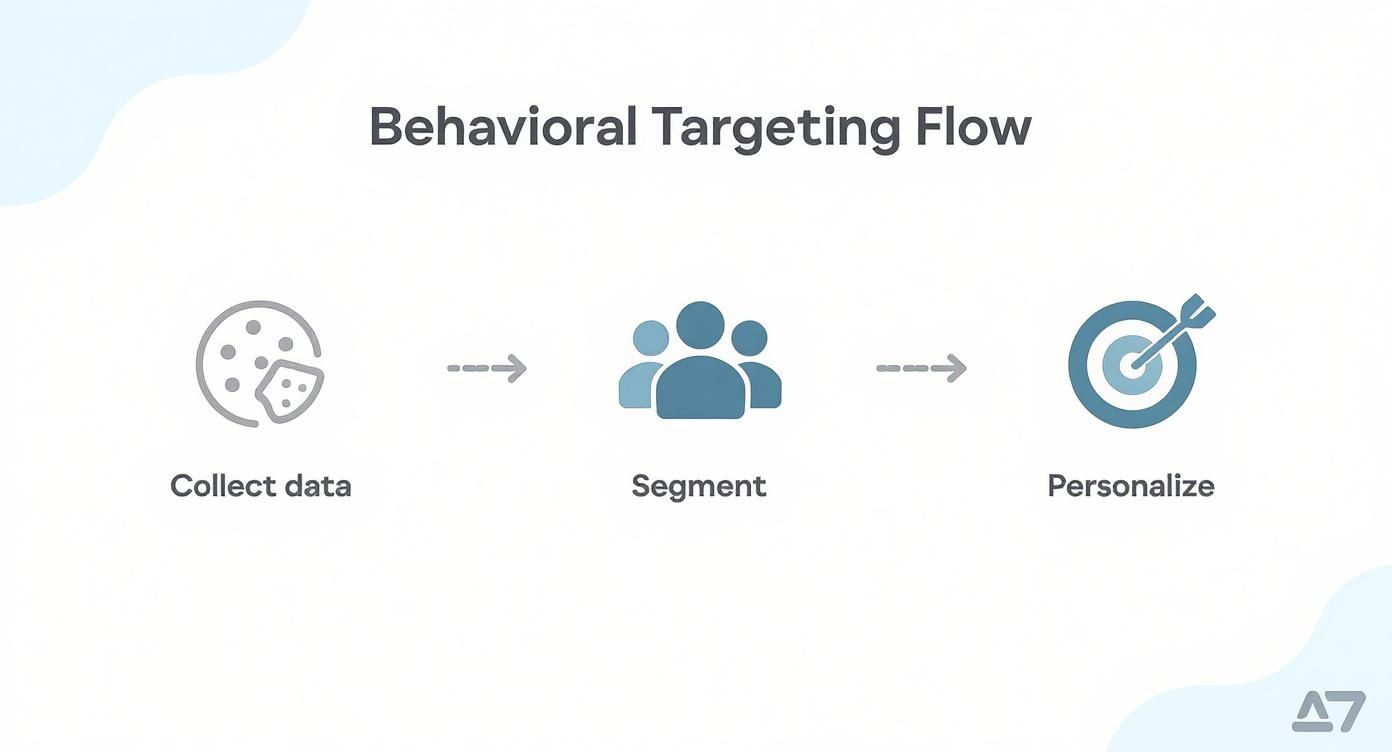
As you can see, the whole point is to turn a bunch of scattered actions into focused, actionable audience groups you can actually do something with.
Matching Ads and Optimizing Performance
Once those segments are defined, the ad platforms can start doing their ad matching in real-time. When a user from that "Active Runner" segment visits a website with ad space, an automated auction kicks off behind the scenes. Brands that want to reach this audience place bids to show their ad, and the winning ad—maybe for a new pair of running shoes—is displayed instantly.
Finally, the process comes full circle with campaign optimization. Marketers watch the performance data to see which ads are actually driving sales and which ones are falling flat. This constant feedback loop allows them to tweak their segments, test out new ad creative, and sharpen their targeting to get better results over time.
This explosion in targeting tech is tied to the broader behavior analytics market, which was valued at $1.10 billion in 2024. It’s projected to hit $10.80 billion by 2032, which shows just how much companies are betting on understanding exactly what their customers want.
Real-World Examples of Behavioral Targeting
The theory is one thing, but seeing behavioral targeting out in the wild is where it really clicks. You’ve run into it hundreds of times, probably without even noticing. It's woven so deeply into the fabric of the modern internet that it quietly shapes what you see on your favorite sites every single day.
From the running shoes that follow you from site to site to the next binge-worthy show that magically appears in your queue, behavioral targeting is the engine personalizing your digital life. It works by connecting a specific action you take to a tailored, automated response.
E-commerce Personalization
Online retail is where behavioral targeting really flexes its muscles. Think about the last time you landed on Amazon. That homepage wasn’t a generic storefront; it was a unique display built specifically for you based on your recent digital footprint.
- Product Recommendations: If you spent Tuesday browsing for a new tent and a sleeping bag, you can bet that by Wednesday, your "Recommended for You" section will be filled with camping gear. Amazon's algorithm saw your interest and immediately adjusted its suggestions to match.
- Abandoned Cart Reminders: Ever add something to your cart, get distracted, and leave? A few hours later, you’ll probably get an email or see an ad for that exact product on social media. That’s not a coincidence; it's a direct, automated nudge to bring you back and complete the purchase.
This kind of hyper-relevant experience is a core pillar of modern marketing personalization strategies, turning a generic shopping trip into a guided journey.
Travel and Hospitality Offers
Travel sites like Expedia are absolute masters of this. Booking a trip isn’t a single action—it’s a whole series of them. You research flights, then hotels, then maybe a rental car. Each step leaves a breadcrumb trail of intent, and these platforms are brilliant at following it.
Let's say you search for flights to Miami for the first week of December. The system doesn't just show you flights; it logs that intent. Over the next few days, you'll start seeing targeted ads on Instagram and other sites for hotels and car rentals in Miami for those exact dates. The system correctly read your flight search as a strong signal and responded with relevant, timely offers to help you build out the rest of your trip.
Entertainment and Content Curation
Streaming services have literally built their empires on sophisticated behavioral targeting. Platforms like Netflix and Spotify don't just dump a library of content on you; they meticulously curate it based on what you’ve watched and listened to before.
Netflix’s interface is a perfect example, showcasing personalized recommendations that are a direct result of analyzing your viewing habits.

This is your past behavior in action. If you watched three sci-fi thrillers in a row, the algorithm takes that as a cue and bumps similar titles to the top of your "Top Picks for You" row. It’s all designed to make sure the content you see is exactly what you’re likely to click next.
To see how this plays out in even more industries, check out these 7 powerful behavioral targeting examples.
Navigating Privacy and Ethical Marketing
With great targeting power comes great responsibility. Yes, behavioral targeting can create shockingly relevant experiences for users, but it also walks a very fine line. The difference between a helpful suggestion and an invasive ad is paper-thin, and crossing it is the fastest way to demolish customer trust.
Let's be clear: successfully using behavioral targeting means putting user privacy first. This isn't just a "nice to have"—it’s a legal minefield. Regulations like Europe's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have completely changed the rules of the game for how businesses collect and use consumer data.
These laws hand the controls back to consumers, giving them the right to know what's being collected and, crucially, the right to say "no." For marketers, that makes transparency non-negotiable.
Building Trust Through Ethical Practices: An Actionable Framework
Operating ethically here isn't about dodging fines. It's about building real, sustainable relationships with customers who feel respected, not tracked. It requires a proactive game plan.
Here’s an actionable framework to make your campaigns both effective and ethical:
- Be Radically Transparent: Your privacy policy shouldn't read like a legal textbook. Clearly explain what data you're collecting and exactly how you plan to use it. No jargon, no excuses. Action: Create a simple, one-page summary of your data practices that users can easily find.
- Make Opting Out Easy: A hidden unsubscribe link or a confusing preferences page is a dark pattern. Give users a clear, simple way to manage their data and opt out of tracking. Action: Place a "Manage My Data" link in your website footer and email footers.
- Lock Down Your Data: You're the guardian of your customers' information. Invest in serious security to protect it. A data breach is a disaster for your customers and a potential death blow to your brand's reputation. Action: Conduct regular security audits and use encryption for all stored customer data.
When regulations use terms like "fundamental rights and freedoms," you know it's about much more than just ticking a compliance box. It’s about building your marketing on a foundation of respect.
The Future in a Cookieless World
This entire conversation around privacy is forcing massive technical changes, with the biggest being the death of the third-party cookie. As major browsers phase them out, marketers have to get smarter and move away from rented third-party data toward more sustainable methods.
The end of third-party cookies doesn’t kill effective targeting. It just kills lazy targeting. This is a massive shift toward higher-quality, consent-based data that actually strengthens customer relationships.
This new reality puts a huge spotlight on first-party data—the information you collect directly from your audience on your own website, app, or CRM. It's cleaner, more accurate, and gathered with explicit user consent, making it the most powerful and privacy-friendly asset you have for creating personalized experiences.
This isn't just a hypothetical shift; it's already shaping the market. For instance, North America is still the leader in behavioral targeting, but growth in Europe is slower precisely because of strict GDPR rules. Yet, European consumers still want personalized experiences—they just have to be delivered with privacy at the forefront. You can get more insights on how privacy is shaping the behavioral targeting market over on dataintelo.com.
How to Implement a Behavioral Targeting Strategy

Alright, let's move from theory to action. Putting behavioral targeting into play isn't magic; it's a structured process of turning raw user data into real business results. Think of this as your playbook for launching a campaign that actually works.
It all starts with a simple question: What are you trying to accomplish? Are you fighting to slash abandoned cart rates, trying to boost repeat purchases from loyal customers, or hunting for brand-new users who are ready to buy?
Your answer to that question shapes every single decision that follows. It dictates the platforms you use, the audiences you build, and the ads you write. Without a goal, you're just hoarding data. With one, every click has a purpose.
Setting Your Technical Foundation
Before you can target a single soul, you need the right plumbing in place. This is the technical backbone of your entire strategy, and it starts with installing tracking pixels or tags on your website from platforms like Meta or Google Ads.
These tiny snippets of code are your eyes and ears. They anonymously track how people interact with your site—what pages they view, what they add to their cart, and what they ultimately purchase. This information is the fuel for your targeting engine.
Getting this setup right is non-negotiable. If your data collection is flawed, your targeting will be, too. That means wasted ad spend and missed opportunities.
Building and Activating Your Audience Segments
With your pixels firing and data flowing in, the real fun begins: audience segmentation. This is where you stop shouting at everyone and start having meaningful conversations with specific groups based on what they’ve done.
Instead of a one-size-fits-all message, you can create distinct buckets of users who have shown different levels of interest.
Here are a few essential segments every business should start with:
- Website Visitors: This is your broadest group—everyone who stopped by your site in the last 30-90 days. It’s a solid choice for general brand awareness campaigns.
- Product Viewers: These folks browsed specific product pages but never added anything to their cart. They’re curious but need a gentle nudge back.
- Cart Abandoners: The holy grail of retargeting. This high-intent group added items to their cart but got distracted. They are your warmest leads, so don't let them get away.
- Past Purchasers: Your existing customers. You can re-engage them with complementary products, special offers, or loyalty rewards to encourage repeat business.
To make this work across all your channels, you need a single source of truth. A deep customer data platform integration is often the key to ensuring your email, ads, and on-site messaging are all working from the same playbook.
Launching and Optimizing Your Campaigns
Once your segments are ready, it's time to craft ads that speak directly to each group. The ad you show a cart abandoner should feel completely different from the one you show a first-time visitor. Personalize your copy, images, and offers to reflect where they are in their journey.
For a cart abandoner, you might show them the exact product they left behind, maybe with a small discount to seal the deal. For a new visitor, you’d introduce your brand’s big-picture value or showcase your best-selling items.
But launching the campaign is just the beginning. The real work is in the continuous measurement and optimization. Keep a close eye on your key metrics, like conversion rate and return on ad spend (ROAS). This data is your feedback loop, telling you which segments are hitting the mark and which ads are falling flat. Use those insights to shift your budget and refine your approach for maximum impact.
Actionable Checklist for Your First Campaign
To tie this all together, here's a simple checklist to guide you through setting up your first behavioral targeting campaign.
| Step | Key Action | Tool/Platform Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Goal | Pinpoint a specific outcome (e.g., "Reduce cart abandonment by 15%"). | Your internal strategy document or project management tool. |
| 2. Install Pixels | Add tracking tags to every page of your website. | Google Tag Manager, Meta Pixel Helper (Chrome Extension). |
| 3. Build Segments | Create core audiences like "Cart Abandoners (7 Days)" or "All Visitors (30 Days)." | Google Ads Audience Manager, Meta Ads Audiences. |
| 4. Create Ads | Design unique ad copy and visuals for each segment. | Canva for creative, your ad platform's native ad builder. |
| 5. Launch & Monitor | Go live and track key metrics like ROAS and conversion rate daily. | The analytics dashboards within Meta Ads or Google Ads. |
| 6. Optimize | Pause underperforming ads and reallocate budget to winning segments. | Use A/B testing features within your ad platform. |
Following these steps provides a clear, repeatable process for turning user behavior into tangible growth. Don't overcomplicate it at first—just get the fundamentals right, and you'll be well on your way.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Once you start wrapping your head around behavioral targeting, a few questions almost always come up. Let's tackle them right now so you have a crystal-clear picture of how this all works in the real world.
Behavioral Targeting vs. Retargeting: What's the Real Difference?
This is a classic, and for good reason. It’s easy to get them mixed up, but the distinction is actually pretty simple. Think of retargeting as a specific tactic and behavioral targeting as the overall strategy.
- Retargeting is about showing ads only to people who have already visited your website. It's a follow-up conversation.
- Behavioral targeting is the entire playbook. It includes retargeting but also uses browsing habits across the wider web to find new audiences who have never heard of you but fit your ideal customer profile.
So, all retargeting is a form of behavioral targeting, but not all behavioral targeting is retargeting.
Is This Still a Thing Without Third-Party Cookies?
Absolutely, but the game is definitely changing. The slow fade of third-party cookies doesn’t kill the strategy; it just makes your first-party data—the information you collect directly from your audience—insanely valuable.
The end of third-party cookies isn't an obstacle. It's an upgrade—a shift toward higher-quality, consent-based marketing that builds real trust with customers.
Smart marketers are already leaning into this. They're using the data they own, combining it with contextual targeting, and exploring new privacy-first technologies that keep users in control. The actionable takeaway is to start building your first-party data assets now, through things like email newsletters, user accounts, and loyalty programs.
How Do I Know If It's Actually Working?
Clicks and impressions are easy to count, but they don't pay the bills. If you want to know if your campaigns are truly making a difference, you need to measure the metrics that tie directly to business results.
Instead of getting lost in vanity numbers, zero in on these three:
- Conversion Rate: What percentage of people are actually taking the action you want them to take, like buying a product or signing up?
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): Simple and powerful. How much does it cost you, on average, to win a new customer?
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): For every single dollar you put into your advertising, how many dollars in revenue do you get back?
Focusing on these tells you the real story. They give you a clear, actionable picture of how your campaigns are impacting the bottom line.
Ready to turn user insights into measurable growth? marketbetter.ai provides an integrated AI platform to optimize your audience segmentation, content personalization, and campaign management. Discover how you can build more effective campaigns by visiting https://www.marketbetter.ai.