What Is Audience Segmentation? A Practical Growth Guide
Audience segmentation is the difference between shouting into a crowded stadium and having a real conversation. It's the actionable strategy that stops you from broadcasting one generic message to everyone and helps you start talking to smaller, specific groups about what they actually care about.
This shift ensures your marketing efforts land with the people who matter most, turning generic outreach into personalized, high-impact communication.
What Is Audience Segmentation and Why Does It Matter?
Imagine you run a high-end coffee shop. You've just sourced some incredible single-origin espresso beans and you need to sell them.
You could take out a generic ad targeting everyone in your city. That’s the "spray and pray" approach—a fantastic way to waste money. It's the equivalent of mass marketing, where the message is broad and the results are unpredictable.

Now, what if you segmented your audience? This is where targeted marketing comes in. You could create a group called "Coffee Connoisseurs"—people who've bought premium beans before or attended your tasting events. Another group might be "Home Baristas," folks who recently bought an espresso machine.
You can now tailor your message. The connoisseurs get an email about a rare new bean. The home baristas get a guide on pulling the perfect shot. Suddenly, your marketing isn't just noise; it's genuinely useful. That’s the entire point of audience segmentation: treating different customers differently because you understand who they are.
The True Cost of Ignoring Segmentation
Skipping segmentation is like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole. You're blasting a one-size-fits-all message at diverse groups with unique problems and motivations. It doesn't just lead to poor results; it can actively annoy potential customers who feel like you don't get them at all.
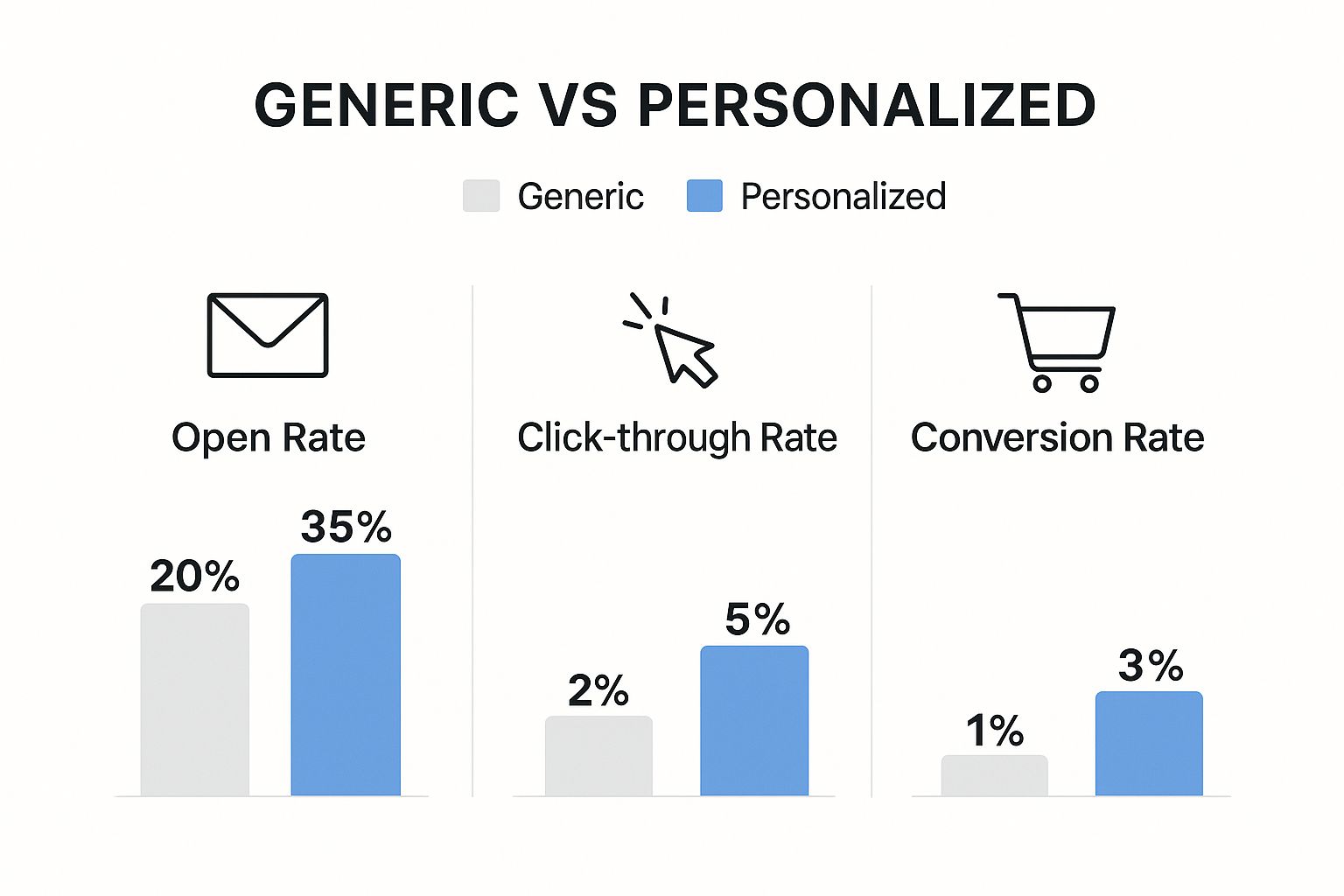
This isn't just a theory; the numbers are staggering. Companies that get this right see a 760% jump in email revenue compared to those that don't. With 81% of consumers saying they're more likely to buy from brands that offer personalized experiences, the case is closed.
In fact, a massive 77% of marketing ROI comes directly from segmented, targeted campaigns. You can explore more data on audience segmentation's impact to see the full picture.
Audience segmentation isn't just a marketing tactic; it's a fundamental business strategy. It transforms your communication from a monologue into a dialogue, building stronger relationships and driving sustainable growth by showing customers you understand them.
Audience Segmentation At a Glance
To make this crystal clear, let's compare the before and after. This table sums up the core ideas behind audience segmentation and why it's a non-negotiable for any business that wants to connect with customers in a meaningful way.
| Concept | Description | Core Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Who | The specific subgroups of your larger audience, defined by shared traits like behavior, location, or interests. | Moves you from speaking to a faceless crowd to engaging with distinct groups of people. |
| What | The process of grouping these individuals using data from your CRM, website analytics, and customer feedback. | Allows you to create targeted campaigns, content, and product offers that are highly relevant. |
| Why | To deliver personalized experiences that increase engagement, boost conversion rates, and foster long-term loyalty. | Improves marketing ROI by focusing resources on the most receptive and valuable customer segments. |
At the end of the day, understanding audience segmentation means recognizing that relevance is the new currency in marketing. When you group your audience thoughtfully, you stop wasting time and money and start building real connections that drive your business forward.
The Four Core Segmentation Methods You Need to Know
Think of understanding your customers like getting to know a new friend. At first, you only know the basics—their name, where they live. That's surface-level stuff. To really get them, you need to understand how they think, what they care about, and what they actually do.
Audience segmentation works the same way. We start with the simple, observable facts and then layer on deeper insights to build a complete picture. These methods aren't just different ways to slice data; they're different lenses for seeing your audience. When you combine them, you move from guessing games to genuine, actionable understanding.
Demographic Segmentation: The "Who"
This is your starting point. Demographic segmentation is the most straightforward way to group people, answering the fundamental question: "Who, exactly, are we talking to?" It categorizes your audience based on objective, easily verifiable attributes.
It's like sorting a deck of cards by suit or number—clear, defined characteristics. For a business, that looks like:
- Job Title: A B2B software company selling project management tools targets "Project Managers" or "Heads of Operations."
- Company Size: An IT provider might create a segment for small businesses with 10-50 employees.
- Age and Gender: A direct-to-consumer brand could target skincare products for women aged 45-60.
- Income Level: A wealth management firm will focus on households earning over $250,000 annually.
Demographics are solid and easy to get, but they only tell you who is buying, not why.
Geographic Segmentation: The "Where"
Next up is geography, which answers the simple question: "Where are these people located?" This isn't just for brick-and-mortar stores. For digital businesses, location dictates everything from language and currency to cultural norms and legal rules.
Think about it: you wouldn't try to sell heavy winter coats to customers in Miami. And a global SaaS company knows that messaging that works in Silicon Valley might need a tweak for an audience in Berlin.
Common geographic data points include:
- Country or Region: Crucial for localization, currency, and compliance.
- Climate: Directly impacts demand for seasonal products.
- Urban vs. Rural: A city-dweller's needs (food delivery, public transport) are wildly different from a rural customer's (gardening supplies, off-road vehicles).
Psychographic Segmentation: The "Why"
This is where it gets really interesting. If demographics are the skeleton, psychographics are the personality. This method digs into the why behind customer choices, grouping people by their values, attitudes, interests, and lifestyles.
Psychographics uncover what truly motivates someone to buy. You could have two people who look identical on paper—say, 35-year-old men with high incomes living in the same city. But one is a risk-averse saver who values security above all else, while the other is an adventurous thrill-seeker who spends his money on experiences. You can't reach both with the same message.
Key psychographic variables look at:
- Values and Beliefs: A brand built on sustainability will naturally attract environmentally conscious consumers.
- Lifestyle: A meal-prep delivery service is a perfect fit for busy professionals who value convenience.
- Interests and Hobbies: A tech company knows to market its new gaming laptop to people who follow esports.
Behavioral Segmentation: The "What"
Finally, we have the most powerful method of all: behavioral segmentation. This one cuts through all the assumptions and focuses on what people actually do. It answers the question, "How is my audience interacting with my brand?"
This is pure, actionable data based on observed engagement. It’s the difference between what someone says they’ll do and their real-world actions.
There are many ways to approach advanced segmentation. While these four are the foundation, experts also look at things like technographic (what tech they use) or transactional data. The key is using the right lens for the job. You can learn more about these different segmentation approaches and see which ones fit your strategy.
Common behavioral data points include:
- Purchase History: Separating frequent, high-value customers from one-time discount shoppers.
- Website Activity: Creating a segment for users who abandoned their carts to send a targeted follow-up.
- Feature Usage: A software company can identify power users of a specific feature and reach out for a case study.
- Email Engagement: Rewarding your most engaged subscribers (the ones who open every email) with an exclusive offer.
Comparing The Four Core Segmentation Methods
To make it even clearer, here's a simple breakdown of how these four methods stack up against each other. Each one provides a different piece of the puzzle, and knowing when to use which is key to building a smart marketing strategy.
| Segmentation Type | What It Answers | Common Data Points | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | Who are they? | Age, job title, income, company size | A B2B SaaS company targeting "Marketing Directors" at firms with 500+ employees. |
| Geographic | Where are they? | Country, city, climate, urban/rural | A retailer promoting snow blowers to customers in the Northeastern US in October. |
| Psychographic | Why do they buy? | Values, lifestyle, interests, beliefs | A sustainable fashion brand targeting consumers who prioritize eco-friendly products. |
| Behavioral | What do they do? | Purchase history, website clicks, email opens | An e-commerce site sending a discount code to users who abandoned their shopping carts. |
Ultimately, no single method tells the whole story. The real power comes from layering these approaches together to create a full, three-dimensional view of your customer.
The most effective strategies rarely rely on a single segmentation method. The magic happens when you layer them. A B2B company might target "Marketing Directors" (demographic) at "SaaS companies in North America" (geographic) who have "downloaded a whitepaper on AI" (behavioral). This creates a highly specific, relevant, and actionable audience segment.
Real World B2B Audience Segmentation Examples
Knowing the different ways to slice up an audience is one thing. Watching those slices turn into actual business results? That's another entirely. The real magic of segmentation happens when you stop thinking in theory and start applying it to solve tangible, everyday business problems. For B2B companies, especially, the shift away from generic, one-size-fits-all outreach can be dramatic.
So, let's get practical. I'm going to walk you through three real-world scenarios showing how B2B teams use segmentation to drive upgrades, sharpen their sales pitches, and find revenue hiding in plain sight.
Each example is broken down into a simple Problem, Solution, and Result. Think of it as a blueprint you can steal for your own challenges. They all build on the four core pillars of segmentation you see below—the different lenses we can use to understand who our customers are and what they need.
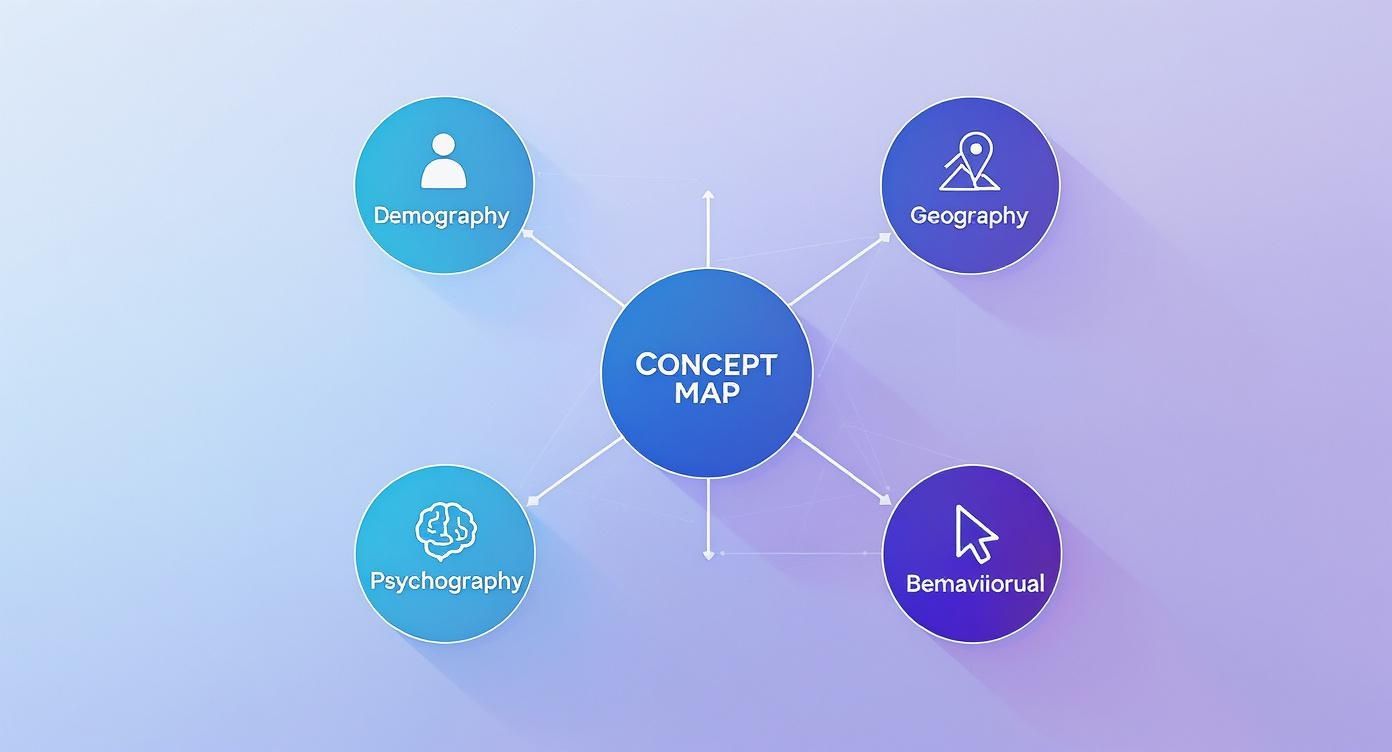
This map is a good reminder that you can view your audience through multiple lenses—from who and where they are to why and how they act.
SaaS Company Driving Upgrades with Behavioral Segmentation
The Problem: A mid-sized project management SaaS company had a problem. A huge chunk of their "Basic" tier users never even clicked on the more advanced features. This meant upgrade rates were flat, and worse, churn risk was high because these users weren't getting the full value. Their generic "Upgrade Now!" emails were going straight to the trash.
The Solution: They stopped blasting everyone and got smart with behavioral segmentation. They split their users into two simple, action-based groups right inside their platform:
- "Power Users": These were the folks constantly hitting the limits of the Basic plan—running out of projects, maxing out storage. They were using every feature available to them.
- "Under-Engaged Users": These customers logged in but stuck to just one or two basic functions, completely unaware of the more powerful tools they had access to.
"Power Users" got campaigns that felt like a secret handshake, showing them exactly how premium features would solve the bottlenecks they were already experiencing. Meanwhile, the "Under-Engaged Users" received gentle, educational content—like short video tutorials—highlighting a single advanced feature that would make their current workflow even better.
The Result: It worked. They saw a 35% increase in upgrades from the "Power Users" group in just three months. They also cut churn by 15% among the "Under-Engaged" segment, simply by helping them get more value from the product.
By focusing on what customers did (behavioral data) instead of just who they were, the company made every message feel relevant. They connected the dots between user actions and business outcomes.
Manufacturing Firm Tailoring Sales Pitches by Industry
The Problem: A manufacturer of industrial automation gear was spinning its wheels. Their sales team was pitching the same generic script to everyone, from car factories to pharmaceutical labs. The message wasn't landing because it failed to address the vastly different pain points and regulations in each sector.
The Solution: The marketing team switched gears to a firmographic segmentation strategy. They looked at their best customers and broke their target market into three core industries. Then, they built a completely separate playbook for each one.
- The automotive segment saw case studies and emails all about boosting assembly line speed and cutting downtime.
- The pharmaceutical segment got content that hammered on precision, FDA compliance, and sterile production—the things that actually keep them up at night.
The Result: By speaking each industry's language, the company boosted its marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) by a massive 50%. Even better, the sales cycle shrank by 20% because prospects were coming to the table already knowing the company understood their world.
Professional Services Firm Cross-Selling with Client History
The Problem: A digital marketing agency offered a full suite of services—SEO, PPC, content—but most clients only ever bought one. They knew they were sitting on a goldmine of cross-sell opportunities but had no systematic way to figure out who to approach and what to say.
The Solution: The agency dug into its own data, segmenting clients based on their transactional and behavioral history. They created a hyper-specific segment they called "SEO-Only Success Stories." These were clients who had seen a huge jump in organic traffic (a behavioral metric) from their SEO service (a transactional metric).
This group then received a highly personalized campaign. It showed them their own success and then explained how adding PPC could instantly capitalize on that newfound visibility to capture high-intent leads. They even wove in testimonials from similar clients, a tactic we break down in our guide on using voice of customer examples.
The Result: The campaign was a hit, converting 25% of those single-service clients into multi-service accounts. This dramatically increased their average client lifetime value without having to go out and find a single new customer.
How to Build Your Audience Segmentation Strategy
Alright, so we’ve covered the what and the why of segmentation. Now for the fun part: actually doing it. Moving from theory to a real, working strategy can feel like a huge leap, but it’s not. It's a step-by-step process, not some massive, all-at-once project.
Think of it like building with LEGOs. You don’t just dump the whole bin on the floor and hope a spaceship appears. You start with a plan, find the right pieces, and click them together thoughtfully. Let’s walk through the five essential steps to build your own strategy from the ground up.

Step 1: Define Your Business Goals
Before you slice up your audience list, you have to answer one simple question: Why are we doing this? What's the business outcome you're trying to drive? Without a clear goal, you’ll end up with a bunch of interesting-but-useless segments.
This goal becomes your North Star. It guides every single decision you make from here on out. Are you trying to:
- Increase customer lifetime value? Then you’ll probably segment based on purchase history to find juicy cross-sell opportunities.
- Reduce churn? That means you'll want to segment by product usage to spot the accounts that are starting to drift away.
- Improve lead conversion rates? Your focus would be on segmenting new leads by their industry or the specific pain point they came in with.
A well-defined goal—like "increase upgrade rates from our 'Freemium' user base by 15% in the next quarter"—provides the focus you need to build segments that actually move the needle. Start with the end in mind.
Step 2: Gather and Analyze Your Data
With your goal locked in, it’s time to find your LEGO bricks. This is all about pulling data from every place your customers interact with you. Good, clean data is the bedrock of any solid segmentation effort.
You’ll find gold in a few key places:
- CRM: This is your home base for firmographics and basic account details like job titles, company size, and location.
- Website Analytics: Tools like Google Analytics or Matomo are treasure troves of behavioral data. You can see which pages people visit, what features they click on, and how long they stick around.
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Don't be afraid to just ask. Direct feedback gives you rich psychographic insights into your customers' actual challenges, goals, and motivations that you can’t get anywhere else.
Once you have the data, you need to centralize it. For a deeper dive, there are great resources on building a data-driven customer segmentation strategy that can help you get this foundation right.
Step 3: Choose Your Segmentation Models
Now you get to decide how to group everyone. This is where you combine the different methods we talked about—demographic, behavioral, firmographic—to create segments that directly serve the goal you set in step one. A classic B2B starting point is to simply mix firmographics with behavior.
Actionable Comparison: Two Common Starting Models
| Model Name | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Value-Based Segmentation | Groups customers by their economic value—past, present, or future. Think high-spend, mid-spend, and low-spend tiers. | Businesses focused on maximizing revenue from existing customers and giving their high-value accounts the white-glove treatment. |
| Needs-Based Segmentation | Groups customers based on the specific problems they're trying to solve or the benefits they want from your product. | Companies with multiple products or features who need to make their marketing and sales messaging hyper-relevant. |
The key is to start simple. Pick one or two models that make sense. You can always get fancier later.
Step 4: Develop Detailed Segment Profiles
Your segments can't just be rows in a spreadsheet. To be useful, they need to feel like real groups of people. This is where you build a simple profile or “persona” for each one, making it dead simple for your marketing and sales teams to know exactly who they’re talking to.
Give each segment a memorable name, like “Tech-Savvy Startups” or “Established Enterprise Accounts.” Then, flesh it out with their key characteristics, common pain points, and what motivates them. This is the step that turns raw data into a practical tool your whole company can rally around.
Step 5: Launch, Test, and Refine
Time to put your work into the wild. Pick one or two of your most promising segments and launch a targeted campaign. This could be anything from a tailored email sequence to a specific ad campaign on LinkedIn or even personalized content on your website.
And then? You measure everything. Track the metrics that matter for your goal—open rates, click-through rates, demo requests, conversion rates. Compare the results for each segment against your old, one-size-fits-all approach.
Segmentation isn't a "set it and forget it" project. It’s a living strategy. You’ll learn, you’ll tweak, and you’ll get better with every campaign. This is a cycle of continuous improvement.
How AI Is Reshaping Audience Segmentation
Manual audience segmentation has its place, but let's be honest—it has limits. It’s a bit like trying to sort a mountain of LEGO bricks by hand. You can group them by color and shape, but you'll miss the subtle patterns and the really interesting combinations.
AI is the supercomputer that sorts the entire pile in seconds, uncovering connections you never knew existed. It elevates segmentation from a static, rule-based chore into a dynamic, predictive engine. Instead of just looking at what customers have done, AI helps you see what they’re likely to do next.

This isn't just a minor tweak; it's a fundamental shift. We're moving beyond simple groupings to create fluid segments that adapt in real time as customer behavior changes.
And the market reflects this. The global AI market is on a trajectory to blast from $22.6 billion in 2020 to $190.6 billion by 2025. This explosive growth is driven by businesses like yours adopting AI-powered tools to make sense of overwhelmingly complex data.
From Reactive to Predictive Segmentation
The biggest change AI brings to the table is the move from being reactive to predictive.
Think about it. Machine learning algorithms can chew through massive datasets—purchase history, website clicks, support tickets, social media mentions—and spot hidden correlations a human analyst would almost certainly miss. The system learns which signals are most likely to predict a future action, like a purchase or, just as importantly, a cancellation.
This is the heart of predictive segmentation, a way of grouping customers based on their likelihood to do something.
- Traditional Segmentation: "Let's pull a list of customers who haven't bought anything in 90 days." This is reactive. You're looking backward.
- Predictive Segmentation: "Let's find customers who are showing the same behavioral red flags as the ones who churned last quarter—even if they just bought something yesterday." This is predictive. You're looking forward.
AI doesn't just categorize your audience; it forecasts their future needs. This lets you step in with the right message before a customer decides to look elsewhere or cancel their plan. It's a massive competitive advantage.
This analytical firepower is a game-changer for marketers. To see how this works under the hood, check out our guide on predictive analytics in marketing.
Hyper-Personalization at Scale
The other huge win from AI segmentation is hyper-personalization.
Traditional methods might let you personalize an email with a customer's name and recommend a product based on their last purchase. That’s a good start, but AI takes it leagues further. It can analyze an individual's entire journey with your brand and create a "segment of one."
This means the website content, product recommendations, and marketing messages can all change dynamically for each person. It’s the difference between a store clerk who remembers your last purchase and a personal shopper who knows your style, your budget, and what you’ll be looking for next season.
Comparing Personalization Approaches
| Aspect | Traditional Personalization | AI-Powered Hyper-Personalization |
|---|---|---|
| Data Used | Basic demographics, past purchases | Entire customer journey, real-time behavior, predictive scores |
| Execution | Manual, rule-based campaigns ("If this, then that") | Automated, dynamic content that adapts to each user's actions |
| Outcome | Relevant content ("You bought X, you might like Y") | Anticipatory experiences ("We know you like X, so here’s an exclusive look at Z before it launches") |
This level of granular targeting used to be the exclusive domain of giants like Amazon or Netflix. Not anymore. Modern platforms are making it accessible for everyone.
For example, AI's impact extends well into lead generation, where it can dramatically improve how you segment and target prospects. It's why so many companies are now adopting AI-powered lead generation strategies to find high-value leads with far greater precision. This shift from broad targeting to individual engagement is how modern businesses build deeper, more profitable customer relationships.
Common Segmentation Mistakes to Avoid
So, you've decided to get serious about audience segmentation. That’s a huge step. But like any powerful strategy, there are a few classic ways it can go sideways. Knowing what segmentation is also means knowing where the landmines are buried.
Think of this as your field guide to sidestepping the traps that can turn a brilliant plan into a complicated mess. Nail these, and your segments will stay sharp, actionable, and tied directly to your business goals. Let's walk through the most common mistakes I've seen and a simple "Instead of This, Do That" fix for each one.
Over-Segmenting Your Audience
It’s tempting, I get it. You have all this data, and it feels productive to slice and dice your audience into a dozen or more hyper-specific groups. This is a classic rookie mistake. While it looks precise on a spreadsheet, you've just created a management nightmare. There's no way your team can create unique, meaningful campaigns for every single micro-segment.
Instead of: Creating 15 micro-segments that are impossible to manage. Do This: Focus on 4-6 high-impact segments that represent distinct, valuable groups. Prioritize quality and actionability over sheer quantity.
This approach lets you give each important segment the attention it deserves. It keeps you from letting the whole strategy collapse under its own weight.
Using Outdated or Stale Data
Your audience isn't frozen in time—people change, companies evolve, and priorities shift. A segment you built on data from six months ago might be completely useless today. Relying on old information is like navigating with an old map. You're going to get lost.
This is how you end up with misaligned messaging and wasted ad spend. The contact who was a "New Lead" last quarter might be a "Loyal Advocate" now. They need to be treated that way.
Stale vs. Fresh Data: The Bottom Line
| Mistake | The Painful Consequence | The Simple Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Relying on old data | Your messaging feels tone-deaf and irrelevant, killing engagement and conversions. | Refresh your data quarterly. Put a recurring reminder on your calendar to re-pull analytics and review your segment rules. |
| Ignoring real-time signals | You miss golden opportunities to engage customers at critical moments, like right after a purchase. | Integrate real-time behavioral triggers. Use marketing automation to move contacts between segments based on what they just did. |
Creating Segments That Aren't Distinct
Here’s another common pitfall: building segments that bleed into each other. If your "Budget-Conscious SMBs" and your "Early-Stage Startups" groups are filled with mostly the same companies, your segments aren't different enough to matter. They lack clear lines.
Every segment should have unique DNA and require a distinct marketing angle. The sniff test is simple: if you can send the exact same email to two different segments, they probably shouldn't be two different segments.
- Instead of: Having segments with 70% audience overlap.
- Do This: Make sure each segment is clearly defined and mutually exclusive. Run a test on your criteria to confirm that less than 10% of your audience could reasonably fit into multiple segments. This clarity is what makes your targeting lethal.
By sidestepping these common errors, you're not just creating complexity. You're building a segmentation framework that’s tough, smart, and actually drives business results.
A Few Common Questions on Audience Segmentation
Jumping into segmentation usually brings up the same handful of questions. Let's tackle them head-on so you can move from theory to practice with confidence.
How Many Segments Should I Actually Create?
It’s easy to fall into the trap of creating a dozen hyper-specific segments, but that just creates noise and a ton of extra work. A good rule of thumb? Start with three to five high-impact segments.
Focus on the groups that will move the needle the most. Think "High-Value Repeat Customers," "At-Risk Churn Accounts," or "New Leads from Top-Tier Industries." You can always get more granular later, once you’ve nailed the process of targeting these core groups.
Audience vs. Market Segmentation—What’s the Real Difference?
This is a big one, and the distinction is crucial. The easiest way to think about it is with an analogy.
- Market Segmentation: This is like looking at a map of the entire country. You're dividing the total potential market into logical groups, including millions of people who have never even heard of your company.
- Audience Segmentation: This is like looking at your personal address book. You're focused on dividing your known contacts—the people already in your world, like existing customers, leads, and email subscribers.
The key difference is scope. Market segmentation is for high-level strategy, like product development or new market entry. Audience segmentation is for tactical marketing and communication with the people you can already reach.
How Often Should I Revisit My Segments?
Your segments aren't a "set it and forget it" project. People's needs and behaviors change, so your segments need to keep up. A good rhythm is to review them quarterly or right after any major marketing campaign.
When you do, ask yourself a couple of simple questions: Are these groups still distinct from one another? Are they still driving the results we expect? This regular check-in keeps your strategy sharp and prevents you from making decisions based on old, outdated assumptions.
Ready to stop guessing and start targeting with precision? marketbetter.ai uses AI to uncover your most valuable audience segments, automate personalized campaigns, and drive real growth. Discover how our AI-powered marketing platform can transform your strategy at https://www.marketbetter.ai.